What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Understanding How the Endocannabinoid System Works and Its Connection to Gut Health
Choose Your Subscription
Save more with longer commitments
✓ Cancel anytime • ✓ 30-day money-back guarantee • ✓ Free shipping
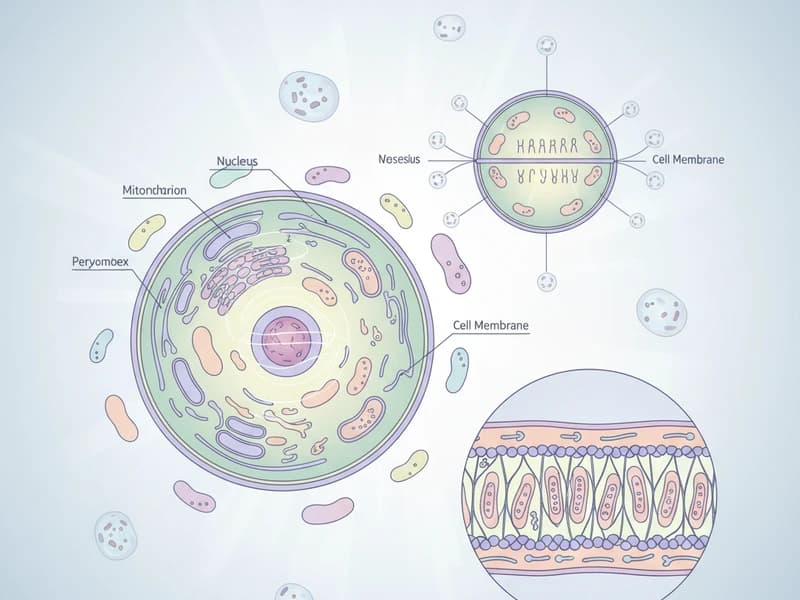
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling network discovered in the early 1990s. It exists in all vertebrates and plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis— your body's internal balance.
The Three Components of the ECS
1. Endocannabinoids (Endogenous Cannabinoids)
Anandamide (AEA) — Named from the Sanskrit word "ananda" meaning "bliss." Regulates mood, stress, pain, and appetite.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) — The most abundant endocannabinoid. Involved in immune function and synaptic plasticity.
2. Cannabinoid Receptors
CB1 — Primarily in the central nervous system (brain, spinal cord). Regulates mood, memory, appetite, pain perception.
CB2 — Primarily on immune cells and peripheral tissues. Regulates inflammation and immune response.
3. Enzymes
FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) — Breaks down anandamide
MAGL (monoacylglycerol lipase) — Breaks down 2-AG
NAPE-PLD, DAGL — Synthesize endocannabinoids
The "Expanded Endocannabinoidome"
Beyond CB1 and CB2, researchers now recognize the "endocannabinoidome"— a broader network that includes:
- PPAR receptors (α, γ, δ) — Nuclear receptors activated by endocannabinoid-like molecules
- TRPV1 channels — Ion channels involved in pain and temperature sensing
- GPR119, GPR55 — G-protein coupled receptors with cannabinoid activity
- N-Acylethanolamines (NAEs) — PEA, OEA, SEA (endocannabinoid analogs)
🔑 Key Insight: The ECS isn't just about "getting high" (that's THC from cannabis plants). Your body makes its own cannabinoids constantly to regulate stress, pain, inflammation, appetite, sleep, and immune function. It's one of the most important regulatory systems in your body.
The Gut-Microbiome-ECS Connection
Here's where it gets fascinating: Your gut microbiome directly controls your ECS.
🔬 Landmark Discovery
In 2010, researchers Muccioli, Cani, and colleagues published groundbreaking work showing that gut microbiota modulate the intestinal endocannabinoid system tone, which regulates gut permeability and systemic inflammation.
Muccioli et al., "The endocannabinoid system links gut microbiota to adipogenesis," Molecular Systems Biology (2010)
How Gut Bacteria Influence the ECS
1. Produce Metabolites That Activate ECS Components
Gut bacteria ferment fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which can reduce FAAH expression → higher anandamide levels. They also produce compounds that engage PPAR receptors and modulate CB1/CB2 expression.
2. Control Gut Barrier Integrity
A healthy microbiome strengthens tight junctions. Endocannabinoids like anandamide activate CB1 receptors on gut cells → triggers GLP-2 release → fortifies the gut barrier. When your microbiome is disrupted (dysbiosis), this protective mechanism fails → leaky gut → LPS enters bloodstream → triggers CB1 overactivation systemically.
3. Regulate Systemic Endocannabinoid Tone
In obesity and metabolic disease, dysbiosis leads to metabolic endotoxemia(high LPS) → overactive CB1 in adipose/liver → fat storage and insulin resistance. Restoring a healthy microbiome with probiotics/prebiotics normalizes this CB1 overactivation.
4. Influence Brain ECS via Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve connects your gut to your brain and expresses CB1 receptors. Gut bacteria produce metabolites that stimulate vagal afferents → modulate central ECS in brain regions like the amygdala (anxiety/stress) and prefrontal cortex (cognition/mood).
The Vicious Cycle (and How to Break It)
Dysbiosis → Leaky gut → ↑ LPS → ↑ CB1 in adipose/liver → Fat storage & inflammation → More dysbiosis
Healthy Microbiome → Strong barrier → ↓ LPS → Normalized CB1 → Balanced metabolism & immunity → Sustains healthy microbiome
✅ Probiotics + Prebiotics can break the vicious cycle and restore healthy ECS tone.
Key Microbial Metabolites That Engage the ECS
What your gut bacteria are producing—and how it affects your endocannabinoid system
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Examples: Butyrate, Propionate, Acetate
Source: FOS + Marine Polysaccharide fermentation
How it works: Butyrate → ↓ FAAH expression (via HDAC inhibition) → ↑ anandamide. Activate GPR43/GPR109A → immune regulation. Stimulate GLP-1/PYY release.
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
Examples: c9,t11-CLA, t10,c12-CLA
Source: L. acidophilus, L. plantarum
How it works: PPAR-γ agonist → anti-inflammatory macrophages. Promotes CB2 signaling. Suppresses colonic inflammation via PPAR-dependent pathways.
Indole-3-Lactic Acid (ILA)
Examples: ILA, Indole-3-aldehyde
Source: L. plantarum, B. lactis (tryptophan metabolism)
How it works: AhR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) agonist → ↑ IL-22 → gut barrier integrity. Reduces neuroinflammation, indirectly supporting ECS balance.
N-Acylethanolamines (NAEs)
Examples: OEA, PEA, SEA
Source: Host production (↑ with healthy microbiome)
How it works: OEA → PPAR-α, vagal afferents (satiety). PEA → CB2 entourage, TRPV1 modulation (analgesia). Levels rise with prebiotic interventions.
Anandamide (AEA)
Examples: N-arachidonoylethanolamine
Source: Host endocannabinoid (↑ with FOS)
How it works: Endogenous CB1/CB2 agonist. Regulates mood, stress, pain, gut barrier. FOS increases intestinal AEA → CB1 → GLP-2 release → tighter gut.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
Examples: Primary endocannabinoid
Source: Host production
How it works: Full CB1/CB2 agonist. FOS normalizes peripheral 2-AG (prevents overactivation in obesity). Critical for immune regulation and synaptic plasticity.
The Strains That Almost Died
How federal budget cuts nearly destroyed a decade of breakthrough research
Academic research programs investigating microbiome-endocannabinoid interactions have faced recurring funding challenges over the past decade. Federal budget sequestration resulted in the discontinuation of several promising research initiatives, despite positive preliminary findings and citations in major scientific reviews.
When research programs are terminated for budgetary rather than scientific reasons, valuable biological samples and strain libraries are typically scheduled for disposal according to institutional biohazard protocols.
In some documented cases, researchers transferred strain samples to academic culture collections or partner institutions to preserve scientific resources. This practice, while controversial from a protocol standpoint, has historical precedent in preserving valuable biological materials during funding transitions.
🧬 Research Context:
Specialized bacterial strains characterized for endocannabinoid-modulating properties represent years of isolation, sequencing, and functional characterization. Publications by Di Marzo (2018) and Russo (2016) reference research from these discontinued programs, demonstrating the scientific value that would have been lost.
Some of this research eventually found its way to commercial applications through academic-industry partnerships. Companies founded by former academic researchers could access strain libraries through legitimate material transfer agreements and published characterization data.
Modern probiotic formulations targeting the endocannabinoid system trace their development to academic research programs that nearly lost funding—demonstrating how basic science can eventually reach practical applications through non-traditional pathways.
Published Research: Probiotics & the ECS
L. acidophilus Upregulates CB2 Receptors (Nature Medicine 2007)
Rousseaux et al.
Finding: Oral administration of L. acidophilus induced significant upregulation of cannabinoid (CB2) and opioid (μ) receptors on intestinal epithelial cells. This resulted in analgesic effects comparable to morphine in visceral pain models.
→ Direct evidence that a probiotic can modulate cannabinoid receptor expression for pain relief.
Microbiota Modulate ECS Tone (Molecular Systems Biology 2010)
Muccioli et al., Cani group
Finding: "Gut microbiota modulate the intestinal endocannabinoid system tone, which in turn regulates gut permeability and plasma LPS levels." Showed that prebiotics restored healthy endocannabinoid levels and receptor expression in obese mice, improving metabolic parameters.
→ Foundational study linking microbiome → ECS → metabolism.
FOS Increases Endocannabinoids for Gut Barrier (Diabetes 2009)
Cani et al.
Finding: Oligofructose (FOS) feeding increased intestinal endocannabinoid production → CB1 activation → GLP-2 release → strengthened tight junctions → reduced gut permeability and plasma LPS. Also normalized adipose CB1 expression.
→ Demonstrates FOS as a direct ECS modulator for metabolic health.
L. plantarum Normalizes Brain ECS (Zebrafish Model 2024)
Prete et al.
Finding: L. plantarum IMC513 restored normal expression of ECS genes (CB1, CB2, FAAH, MAGL) in toxin-exposed zebrafish brains and normalized endocannabinoid levels (AEA/2-AG), providing neuroprotection.
→ Shows gut probiotics can influence central nervous system ECS.
L. paracasei Lpc-37 Reduces Stress & Cortisol (Human Clinical Trial)
"Sisu" study
Finding: L. paracasei Lpc-37 supplementation significantly reduced perceived stress and cortisol levels in healthy adults. Likely mechanism involves preserving central endocannabinoid signaling under stress.
→ Human evidence of probiotic-mediated stress relief via ECS pathways.
Our ECS-Supporting Formula
Each ingredient selected based on published research showing ECS engagement
L. acidophilus La-14
ECS Target: CB2 receptor upregulation
Evidence: Strain-specific (Nature Medicine 2007) - upregulates intestinal CB2 and μ-opioid receptors with morphine-like analgesic effects
Benefits: Gut comfort, pain modulation, produces CLA (PPAR-γ agonist)
B. lactis Bl-04
ECS Target: Barrier integrity & CB1 normalization
Evidence: Species-general - Bifidobacterium strengthens barrier, reduces LPS, normalizes systemic CB1 expression
Benefits: Metabolic balance, reduced inflammation, SCFA production
L. plantarum Lp-115
ECS Target: Brain ECS & eCBome mediators
Evidence: Strain-specific (zebrafish 2024) - normalized brain ECS gene expression; produces CLA and ILA
Benefits: Gut-brain axis, cognitive support, barrier function
L. paracasei Lpc-37
ECS Target: Stress-induced ECS dysregulation
Evidence: Strain-specific (human RCT) - reduced cortisol and perceived stress, likely via preserving central anandamide
Benefits: Stress resilience, mood support, immune modulation
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)
ECS Target: Intestinal endocannabinoid production & CB1 normalization
Evidence: Strongest prebiotic-ECS evidence (Cani 2009, Muccioli 2010) - increases intestinal AEA → CB1/GLP-2 pathway → barrier integrity
Benefits: Metabolic balance, appetite regulation, gut barrier support
Marine Polysaccharide Complex
ECS Target: SCFA production & PPAR activation
Evidence: Seaweed fibers ferment to butyrate/propionate → PPAR-γ/α activation, ↓ FAAH (increases anandamide)
Benefits: Anti-inflammatory, metabolic support, gut microbiome diversity
Targeted Applications of ECS-Supporting Probiotics
Based on the research, here's how our formula may support different health goals
For Your Pet
- ✓ Reduces anxiety & hyperactivity
- ✓ Supports digestive comfort
- ✓ Gut-brain balance for dogs
Digestive Health
- ✓ IBD, IBS, Crohn's support
- ✓ Reduces gut inflammation
- ✓ CB2-mediated relief
General Wellness
- ✓ 40B CFU premium formula
- ✓ Research-backed strains
- ✓ Full ECS support
Frequently Asked Questions About the Endocannabinoid System
Common questions about how the ECS works and its role in gut health
What is the endocannabinoid system?⌄
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system discovered in the 1990s. It exists in all vertebrates and plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis—your body's internal balance. The ECS regulates functions like mood, appetite, pain perception, immune response, and gut health through cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), endocannabinoids (like anandamide), and enzymes that produce and break down these molecules.
How does the endocannabinoid system work?⌄
The ECS works through three main components: (1) Endocannabinoids like anandamide and 2-AG that your body produces naturally, (2) Cannabinoid receptors (CB1 in the nervous system and CB2 in immune cells) that these molecules bind to, and (3) Enzymes like FAAH and MAGL that break down endocannabinoids after they've served their purpose. When activated, the ECS helps regulate everything from stress response to gut barrier function.
What is the endocannabinoid system and gut health connection?⌄
Your gut contains millions of cannabinoid receptors that work with your microbiome to regulate digestion, inflammation, and the gut-brain axis. Research shows that gut bacteria directly influence your ECSby producing metabolites that affect endocannabinoid levels and receptor expression. A healthy microbiome supports optimal ECS function, which in turn maintains gut barrier integrity and reduces inflammation.
How to support your endocannabinoid system naturally?⌄
Support your ECS through: (1) Diet – omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and fermented foods; (2) Exercise – regular physical activity increases endocannabinoid production; (3) Stress management – meditation and yoga support ECS balance; (4) Quality sleep – essential for ECS regulation; and (5) Targeted supplements – like cannabinoid probiotics that enhance your gut's ability to support the ECS naturally.
How cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system?⌄
Cannabinoids—whether produced by your body (endocannabinoids), gut bacteria (through probiotic metabolites), or plants—interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors throughout your body. In the gut specifically, cannabinoid activation helps regulate motility, reduce inflammation, strengthen the intestinal barrier, and modulate immune responses. Probiotic strains can enhance this process by producing metabolites that support your body's own endocannabinoid production.
What are cannabinoid probiotics and how do they work?⌄
Cannabinoid probiotics are specific bacterial strains scientifically shown to modulate the endocannabinoid system. They work by producing metabolites like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), and other compounds that can increase endocannabinoid levels, regulate CB1/CB2 receptor expression, and support gut-brain axis function—all without containing any cannabis or THC.
Ready to Support Your Endocannabinoid System?
Experience the power of probiotics formulated based on ECS research. 60-day money-back guarantee.